
- #PARTITION FIND AND MOUNT HOW TO#
- #PARTITION FIND AND MOUNT INSTALL#
- #PARTITION FIND AND MOUNT PC#
- #PARTITION FIND AND MOUNT WINDOWS#
We will bring more light upon this at the time of speaking of the filesystem in Linux.ĭisk Partitioning in a PC Legacy Partitioning and Booting The Basic PrinciplesĪt the beginning, when disks had little space, there was the idea that four partitions would be enough for all possible usage (but this proved false). Generally they are named /dev/hd/ or /dev/sd/ e.g. In Linux, partitions are named after the path from the unique root of the tree - into which all directories and files (including device files) are placed to constitute the entire filesystem - to their location in this tree.
#PARTITION FIND AND MOUNT WINDOWS#
The Windows system itself is always located in C. In Windows, partitions are named after a letter followed by a colon e.g.One of these partitions is marked in a specific way as the boot partition.

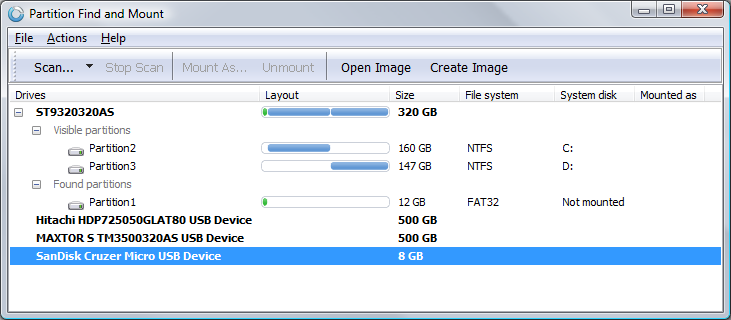
This is why they are referred to as volumes. The different partitions of disks on a machine are seen, regardless of their physical nature, as mass storage volumes. This program is called a partition editor. System administrators can, from the OS that is currently running, use a specialized program to create, delete and manipulate partitions. The partition table contains information about the size and the location of the partitions. To access the partitions, the operating systems have to read a very particular area of the disk, called the Partition Table. Each system can store and retrieve data on these partitions independently from other operating systems. This dividing is done by an operation called partitioning and the created regions are called partitions.
#PARTITION FIND AND MOUNT INSTALL#
It is often necessary - especially when one wants to install several operating systems on the same computer - to divide the hard disk into several regions and to attribute every one of them to such or such operating system. This type of formatting is also known as low-level formatting. This is done to interface with the controller's hardware and firmware. That means that damaged tracks are marked and replacements used, sector numbers are written. The operating systems can not see if a disk is inside the system enclosure, beside it, on a table, or on another shelf, so there is no difference between what some people call internal and external disks.ĭisks are normally supplied formatted by the manufacturer. No matter whether it is a flash device that looks like a disk, an optical drive or a 'real' hard disk, or even a combination of several devices.īecause newer types of mass storage devices present themselves to the system as disks, they fall into this category. a place where they can store and retrieve data perennially - perennially implying the idea of nonvolatility when powering the computer off. In this document, the word disk will be used as a generic term for anything that is seen by operating systems as a disk drive i.e.
#PARTITION FIND AND MOUNT HOW TO#
In this article, I will show you how to mount partitions using UUID and LABEL using the /etc/fstab file on Linux. So, the uniqueness of LABEL depends on how creative you are at naming your partitions. LABEL on the other hand is a short name that you can put it when you format a partition to identify the disk. Even if it’s different computer system, the probability of duplicate UUID is almost zero. UUID is a better choice as it is unique throughout the system. If that happens, your hard drives may be mounted in the wrong mount points resulting data loss or data corruption.
Depending on the order of how you connected the hard drives to your motherboard, it may change. There is no guarantee that /dev/sdb1 will always be /dev/sdb1. Similarly, /dev/sda1 is the first partition of the first hard drive. dev/sdb1 is the first partition of the second hard drive of your computer. Here, /dev/sdb1 is set to mount at the path /storage/disk2p1. dev /sdb1 /storage /disk2p1 ext4 defaults 0 0


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
